 Procurement of Services: Basic Process
Procurement of Services: Basic Process
This section describes the basic process for the procurement of externally performed services.
The following graphic outlines all the possible steps in this process:
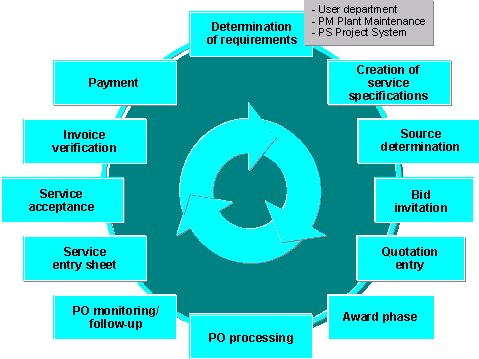
The procurement of services may involve the following steps:
Determination and recording of requirements
Determination of possible sources
Bid invitation procedure
Entry of data from quotations submitted by bidders
Comparison of quotations
Award phase (order placement)
Monitoring of purchase orders
Entry of services actually performed
Acceptance of services performed
Verification of invoices for services
The following sections describe these steps in more detail.
Determination and Recording of Requirements
Determining Requirements
A need for certain services can arise in a user department of your enterprise, within the framework of a project (such as the translation of software) or with regard to regular maintenance work (such as the outsourcing of routine electrical jobs) for instance.
The user department can either prepare a purchase requisition itself, or request Purchasing to do so. In each case, the requisition is the trigger for procurement activities in MM Purchasing.
In the case of large-scale projects involving the use of the SAP application component PS Project System, purchase requisitions with precise performance dates are created from networks. These requisitions are transmitted to the MM Purchasing component automatically. Service specifications from existing standard networks can be utilized to simplify the creation of such networks.
If you use PM Plant Management in your enterprise, specifications for regular maintenance work or servicing will similarly be created outside the MM component and automatically forwarded to MM Purchasing for further processing. The purchase requisition is created without the need for any further entry of data by simply passing on the service specifications from an existing general maintenance task list, or from the maintenance task list for a functional location or piece of equipment, for example.
Recording Requirements
At the time a need is established, a document is created in the system as the basis for the procurement process. This can be a purchase requisition or an external purchasing document such as a request for quotation (RFQ) or a purchase order.
The document can contain a set of service specifications with details of the necessary service or group of services.
In this early phase of the procurement process, however, you also have the option of dispensing with service specifications altogether and only making rough provision for unplanned services by setting value limits .
This method is especially suitable when outside firms are employed, since in this case the precise nature and extent of the relevant services are often unclear until the time they are actually performed.
If you wish to ensure that the dual control principle applies to requisitions (and also purchase orders), you can subject these documents to a release (approval) procedure.
This guarantees, for example, that the goods or services covered by a purchase requisition that exceeds a specified value may not be ordered without the approval, say, of an appropriate technical expert and the responsible head of department. The conditions for the release of a requisition for ordering purposes, and the points in your enterprise (individuals or departments) that must effect release (signify approval) are freely definable.
 Note
Note
To ensure that the release process runs smoothly, you can make use of SAP Business Workflow. This ensures that even users who are unfamiliar with the SAP System can release (approve) purchase requisitions without any trouble by processing a mail in their integrated inbox.
Determination of Possible Sources
As a rule, a live system contains a large volume of purchasing data. In the source determination facility, MM External Services Management offers you an instrument for analyzing this data, enabling you to establish whether suitable potential bidders exist for the requested services and whether longer-term business relationships have already been set up with certain service providers in the form of contracts.
The price simulation function can help you to choose the desired source of supply from the sources suggested by the system. In this case, the requisition can then be converted directly into a standard purchase order or a release order to be issued against a contract that already exists with the service provider.
The system accelerates the award phase by automatically converting requisitions into standard Pos or contract release orders. The routine work involved in assigning sources can thus be eliminated.
In the event that services are requested for which there has previously been no requirement, i.e. for which no source currently exists in the system, a bid invitation process must be carried out.
 Note
Note
MM Vendor Evaluation can simplify the task of searching for a suitable service provider. If you have assigned scores for quality and the timeliness of service performance to the service entry sheets of your existing providers, the analysis and comparison functions of MM Vendor Evaluation provide you with an additional decision criterion.
For more information on this subject, please refer to the MM - Vendor Evaluation documentation.
The Process of Source Determination in the System
Information in various forms is available to the system in the process of determining potential sources for a requested service. The information it uses is as follows (in order of use):
1. Vendor service conditions
The system first checks whether master conditions whose validity period covers the delivery date shown in the purchase requisition exist for the service.
If master conditions exist for one or more vendors, the system suggests these vendors as sources of supply.
The prices and conditions of the relevant master condition are then suggested when you create a PO with reference to the assigned requisition.
2.Contracts
If contracts that either contain the material group or the service shown in the purchase requisition exist in the system, the system suggests these contracts as sources of supply.
If a purchase requisition has been assigned to a contract, the system can generate release orders (call-offs) against it.
 Note
Note
In Customizing for Purchasing, you can define the requirements under which the sources for services are to be determined.
For example, you can specify that a contract is to be suggested as a source if it contains
at least one
service from the requisition. Alternatively, you can specify that a contract is only to be suggested if it covers
all
the requested services.
This means that you decide yourself, on the basis of the data situation in your system, whether the system is to suggest
as many sources as possible
(which may be more or less suitable), from which you then make your choice, or whether the system is to suggest the
ideal
source only.
If your system only contains a small volume of data, the former approach is recommended. If you have a very well maintained system, you will wish to keep the number of suggested sources down and see only the best possible one.
You can also enter the source for a purchase requisition manually. This function enables you to assign the requisition to a provider from whom you have not previously procured services, for example.
Bid Invitation Procedure
The bid invitation phase is divided into two parts. First you create RFQs and then you record the incoming quotation data.
Creating an RFQ
If a bid invitation process is to be initiated for services, an RFQ must be created. In doing so, you can simplify and speed up the data entry process by referencing the preceding document, the purchase requisition.
You can assign the RFQ to any number of different potential bidders. The system creates a separate RFQ for each bidder, each with a unique number. The RFQs are then transmitted to the bidders.
Entry of Data From Quotations Submitted by Bidders
When quotations (bids) are received from bidders, the latter’s prices and conditions are entered in the RFQs that already exist in the system. The status of the RFQs is then changed: the RFQs in fact become quotations.
Comparison of Quotations
When all quotations have been received and entered, the most favorable one is quickly determined using the price comparison list.
The price comparison list evaluates the quotations for you at different levels. You can make your decision on the basis of list of all quotations ranked by total value or compare the quotations at individual outline levels. The system provides you with comparative data right down to the individual service (task or activity) level if required.
When you have identified the most favorable quotation, you award the work (issue a PO) to the bidder of your choice. Rejection letters can be sent to unsuccessful bidders automatically.
Award Phase (Order Placement)
The successful bidder receives either a standard purchase order or a release order issued against an existing contract, either of which is created by conversion of the relevant quotation (i.e. you are making use of already existing data in this case too).
Monitoring of Purchase Orders
During the phase of service performance, the cumulative " actual" values (for the services actually performed) are continually updated in the underlying purchase order (standard PO or contract release order). This enables you to monitor the progress of a procurement project on an ongoing basis.
You can obtain follow-on information on a PO via the monitoring functions PO history and release (order) documentation, and the comparison of planned/actual values within the service specifications. If necessary, you can monitor the completion confirmation for each individual service line.
In addition, the comprehensive analyses provided by the SAP Logistics Information System (LIS) are available to you. These enable you to examine data such as the cost of maintenance measures in the first quarter of the current year and compare the cost situation in that quarter with the situation in the corresponding quarter of the preceding year, for example.
Entry of Services Actually Performed
You enter services that have actually been performed by means of service entry sheets. In doing so, you can reference the PO. This procedure accelerates the entry of planned services in particular. Each individual service is recorded together with quantities and values.
If a value limit for unplanned services has been set in the purchase order, you can maintain specifications for such services at the time you record their actual performance. The services are recorded with their precise value, and the system checks that the limit has not been exceeded.
Acceptance of Services Performed
After services that have been performed for your firm have been recorded in the service entry sheet, one or more responsible persons can check that the work is satisfactory and formally accept the services.
You can separate the process of service acceptance from that of service entry in order to maintain the dual control principle. However, it is also possible to have entry and acceptance carried out by the same individual or department in your enterprise.
You have a choice between different procedures for service acceptance:
The fastest option is acceptance at the touch of a key in the service entry sheet by the person responsible.
However, you also can make service entry sheets subject to a release (approval) procedure .
Depending on the setting in Customizing, there may be different release procedures involving different "release points" (individuals or departments) within your enterprise, each of which must successively signify their approval. The document is not regarded as accepted until the last release point has released it. This procedure enables you to ensure both technical and commercial correctness.
Verification of Invoices for Services
At the conclusion of the procurement process, the service provider’ s invoices are checked for correctness. This involves comparing the value from the accepted entry sheet with that shown in the invoice and checking that the tax amounts are correct. If the value in the entry sheet is exceeded, the system issues a warning message. Invoices that have been verified and released to Financial Accounting are then paid automatically.
 Note
Note
Instead of the conventional method of invoice verification, you can use the Evaluated Receipt Settlement (ERS) procedure. In this case, you do not wait for the service provider to submit an invoice, but create one in the SAP System on the basis of the data in the PO. The service provider receives a credit memo and a log enabling him to check the correctness of the former.
With this, the procurement process for services is concluded.